How Many Access Points Are Used By A Basic Service Set (Bss)?
Like wired networks, wireless networks have different concrete and logical topologies. The 802.11 standard describes different service sets. A service gear up describes how a group of wireless devices communicate with each other.
Each service set uses the Same Service Gear up Identifier (SSID). The SSID is the "friendly" proper noun of the wireless network. It'southward the wireless network name you run into when y'all look at bachelor wireless networks on your wireless device.
In this lesson, I'll explain the unlike service sets, and nosotros'll take a expect at another mutual AP modes.
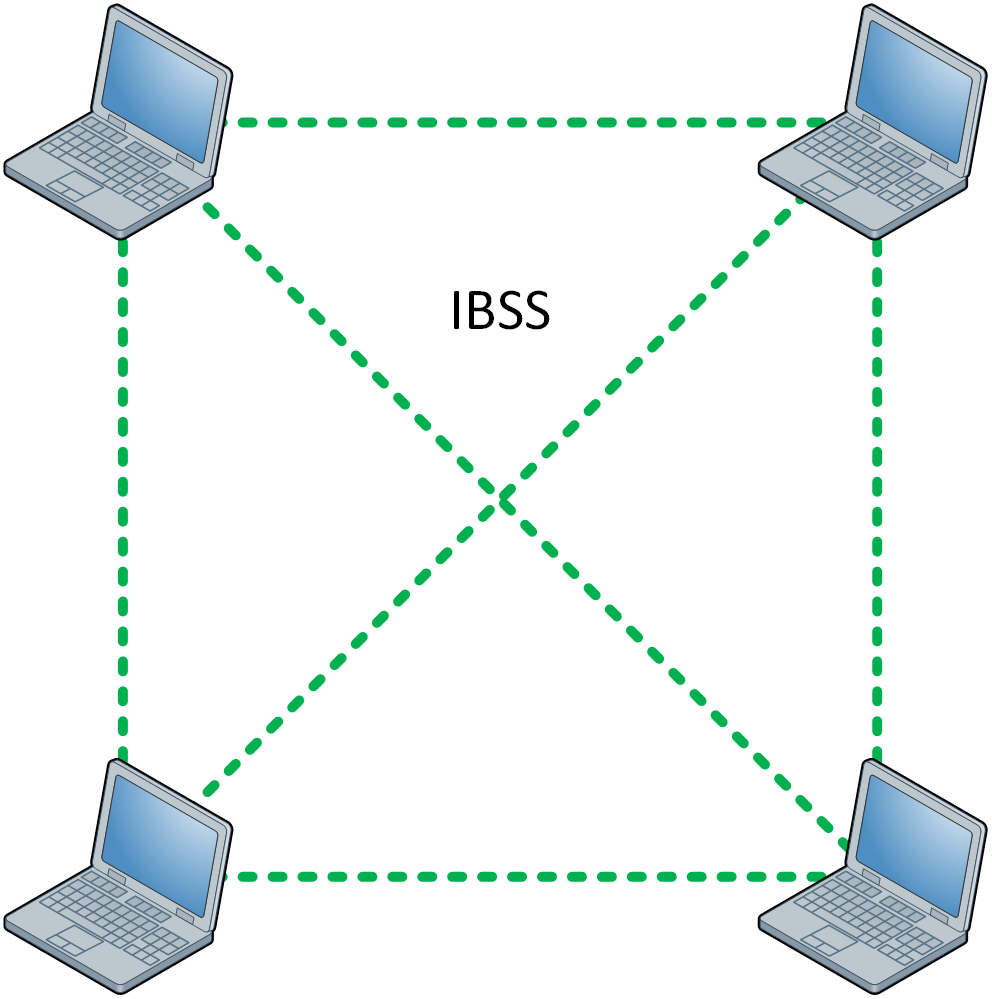
IBSS
With an Independent Basic Service Prepare (IBSS), two or more wireless devices connect direct without an access signal (AP). Nosotros likewise call this an ad hoc network. I of the devices has to start and advertise an SSID, similar to what an AP would do. Other devices tin so join the network.
An IBSS is not a popular solution. You could use this if you want to transfer files between ii or more laptops, smartphones, or tablets without connecting to the wireless network that an AP provides.
Infrastructure Mode
With infrastructure way, we connect all wireless devices to a primal device, the AP. All information goes through the AP. The 802.xi standard describes different service sets. Let's take a look.
Bones Service Set up (BSS)
With a Basic Service Set (BSS), wireless clients connect to a wireless network through an AP. A BSS is what we use for most wireless networks. The idea backside a BSS is that the AP is responsible for the wireless network.
Each wireless customer advertises its capabilities to the AP, and the AP grants or denies permission to join the network. The BSS uses a unmarried channel for all communication. The AP and its wireless clients utilise the same aqueduct to transmit and receive.
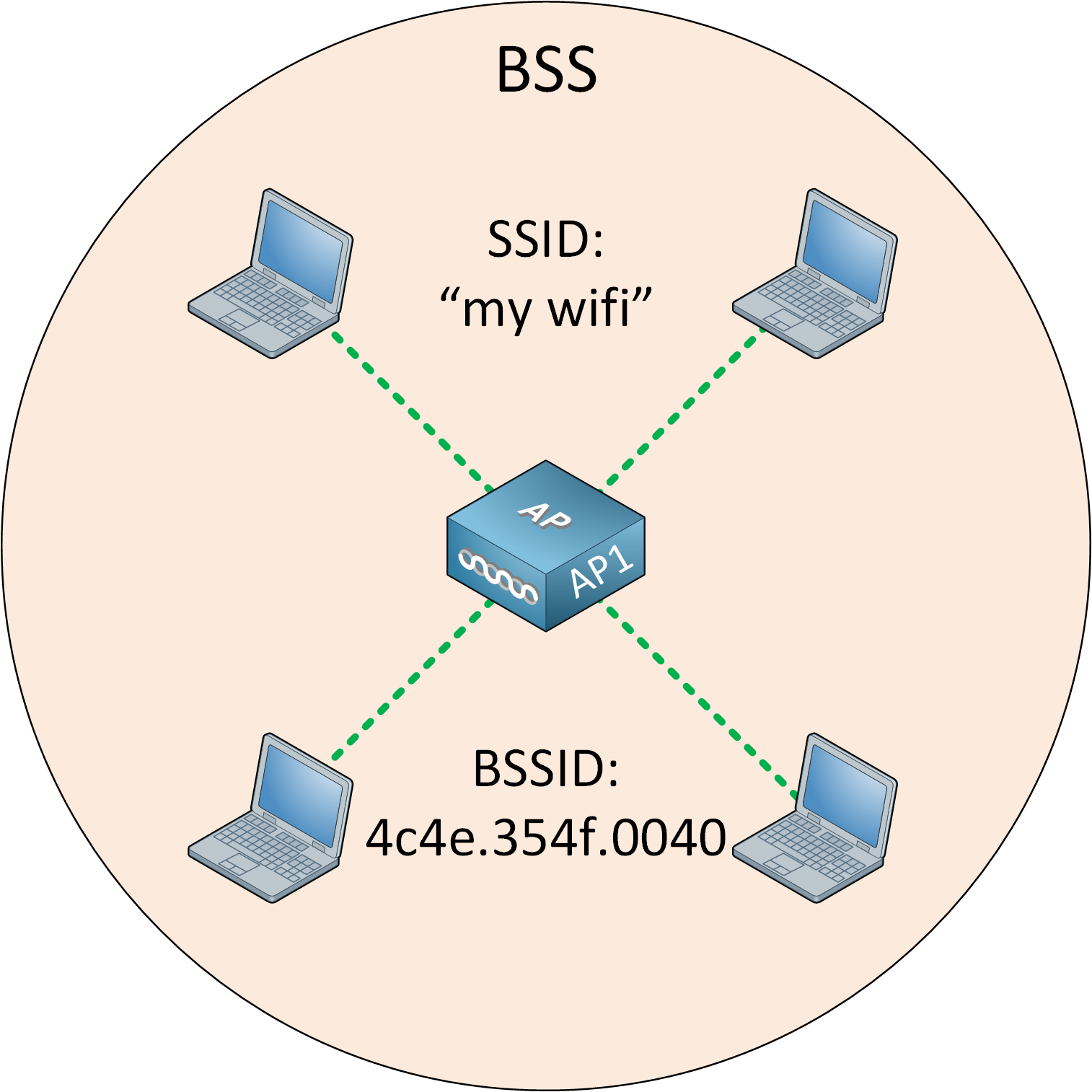
The SSID is the "nice" name of the wireless network, and information technology doesn't have to be unique.
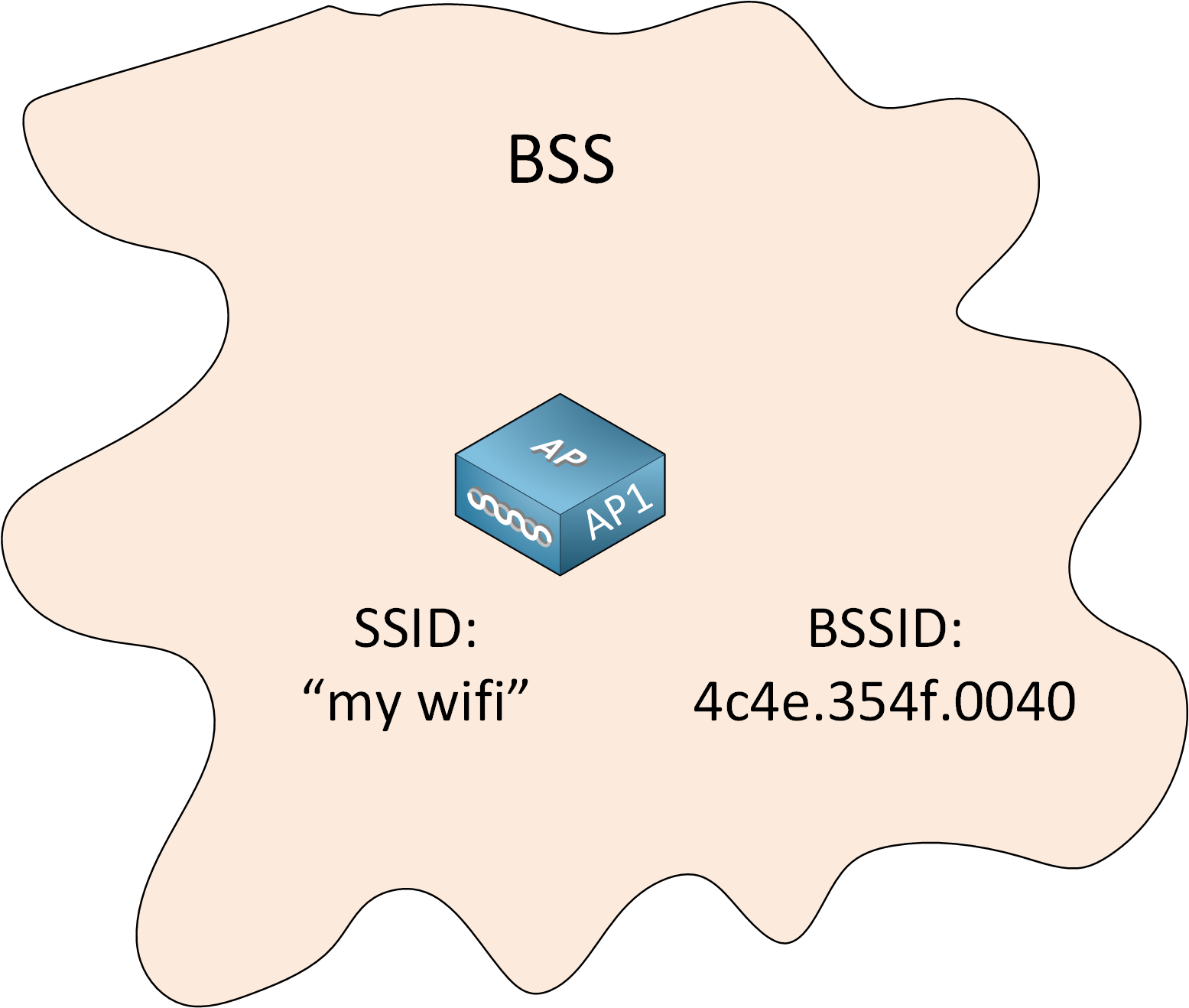
The AP also advertises the Basic Service Set Identifier (BSSID). This is the MAC accost of the AP's radio, a unique address that identifies the AP. All wireless clients have to connect to the AP. This ways the AP'southward betoken range defines the size of the BSS. Nosotros call this the Basic Service Area (BSA).
In the pic above, the BSA is a cute circle. This might be the instance if you install your AP somewhere in the middle of a meadow with nothing effectually the AP. In a building, the BSA probably looks more like this:
When a wireless device wants to join the BSS, it sends an association request to the AP. The AP either permits or denies the asking. When the wireless device has joined the BSS, we call it a wireless client or 802.11 station (STA).
All traffic from a wireless client has to get through the AP even if information technology is destined for some other wireless customer.
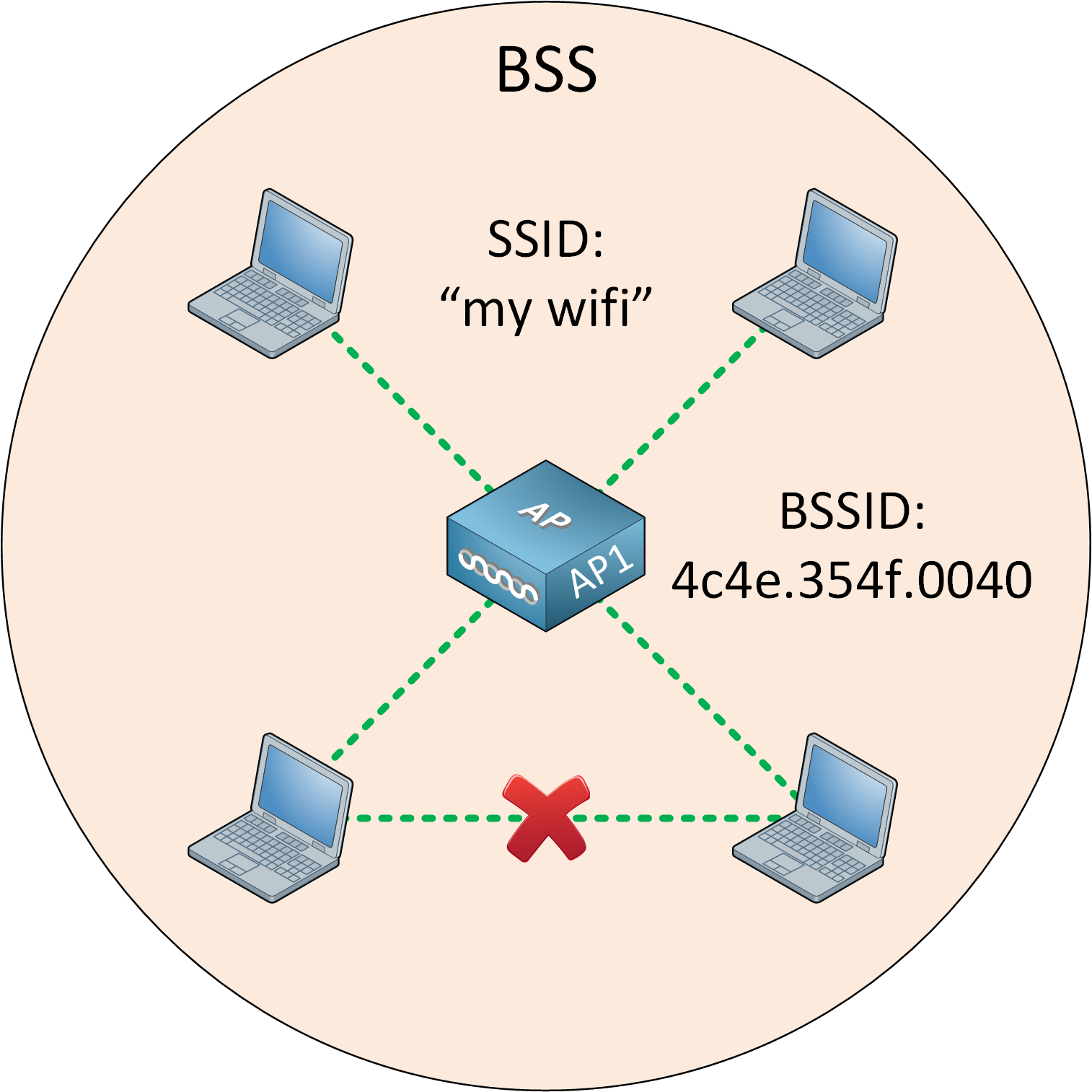
Everything has to become through the AP because the AP is our central point for management, and it limits the size of the BSS. The AP's signal range defines the boundary of the BSS.
Distribution Arrangement (DS)
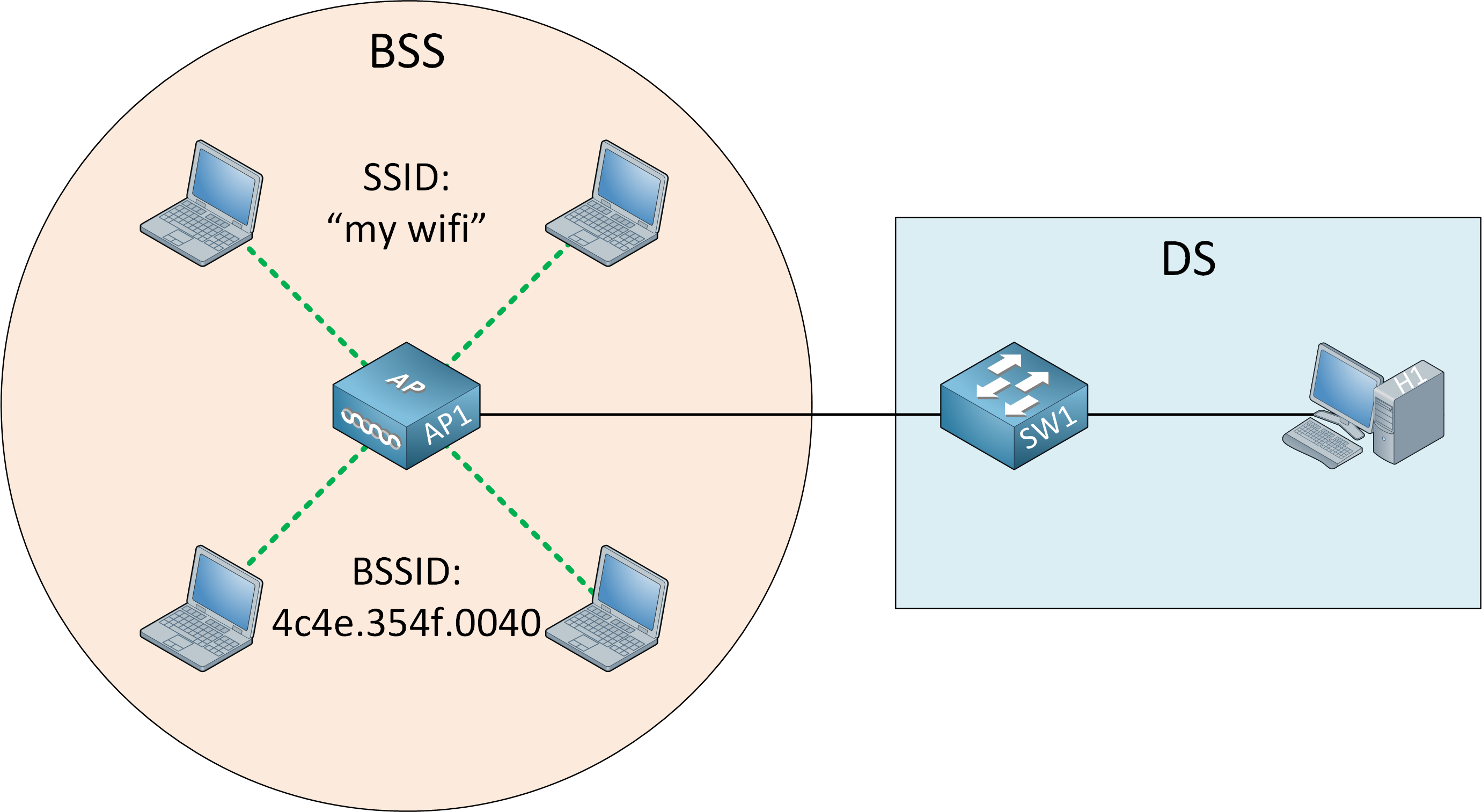
A BSS is a standalone network with a unmarried AP. In the pictures higher up, there is no connection with a wired network.
Most wireless networks, however, are an extension of the wired network. An AP supports both wired and wireless connections. The 802.eleven standard calls the upstream wired network the distribution system (DS).
The AP bridges the wireless and wired L2 Ethernet frames, allowing traffic to catamenia from the wired to the wireless network and vice versa.
We can besides do this with VLANs. The AP connects to the switch with an 802.1Q torso. Each SSID maps to a different VLAN:
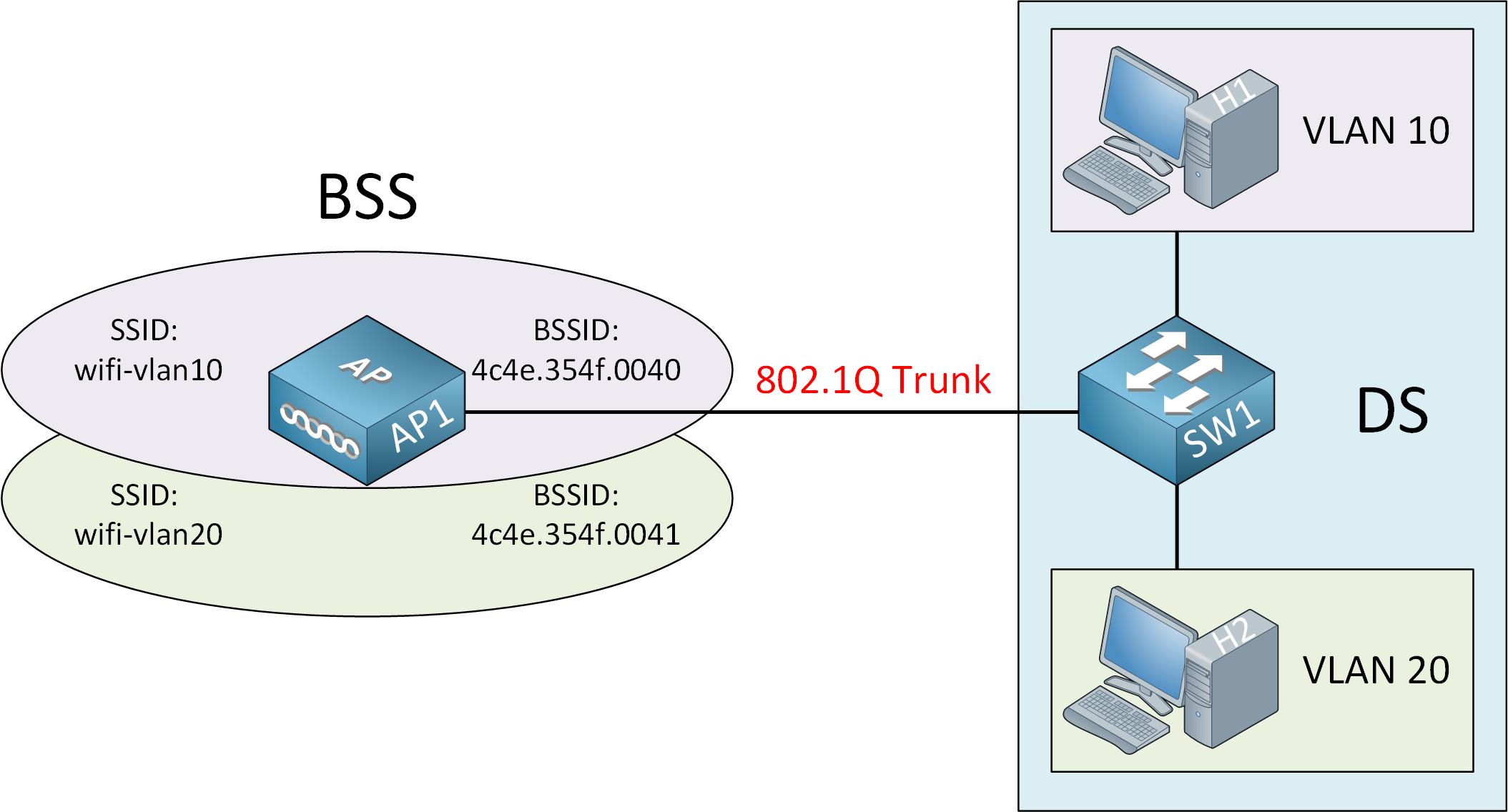
Each wireless network has a unique BSSID. The BSSID is based on the MAC accost, and then nearly vendors (including Cisco) increment the last digit of the MAC accost to create a unique BSSID.
Fifty-fifty though we accept multiple wireless networks, they all use the same underlying hardware, radios, and channels. If y'all accept an AP with multiple radios, so it's possible to assign wireless networks to different radios. For case, you could use 1 wireless network on the 2.iv GHz radio and another one on the five GHz radio.
Extended Service Ready (ESS)
A BSS uses a single AP. This might not exist enough because of two reasons:
- Coverage: A unmarried AP'southward signal can't comprehend an entire floor or building. Yous need multiple APs if you want wireless everywhere.
- Bandwidth: An AP uses a single channel, and wireless is half-duplex. The more active wireless clients you have, the lower your throughput will be. This as well depends on the data rates you support. A wireless client that sits on the edge of your BSA might however be able to reach the AP, merely tin but use depression data rates. A wireless customer that sits shut to the AP can use loftier data rates. The distant wireless client will claim more than "airtime," reducing bandwidth for everyone.
To create a larger wireless network, nosotros use multiple APs and connect all of them to the wired network. The APs work together to create a large wireless network that spans an entire floor or building. The user only sees a single SSID, so they won't detect whether nosotros use one or multiple APs. Each AP uses a dissimilar BSSID, and so behind the scenes, the wireless customer sees multiple APs information technology can connect to. We call this topology with multiple APs, an Extended Service Set (ESS).
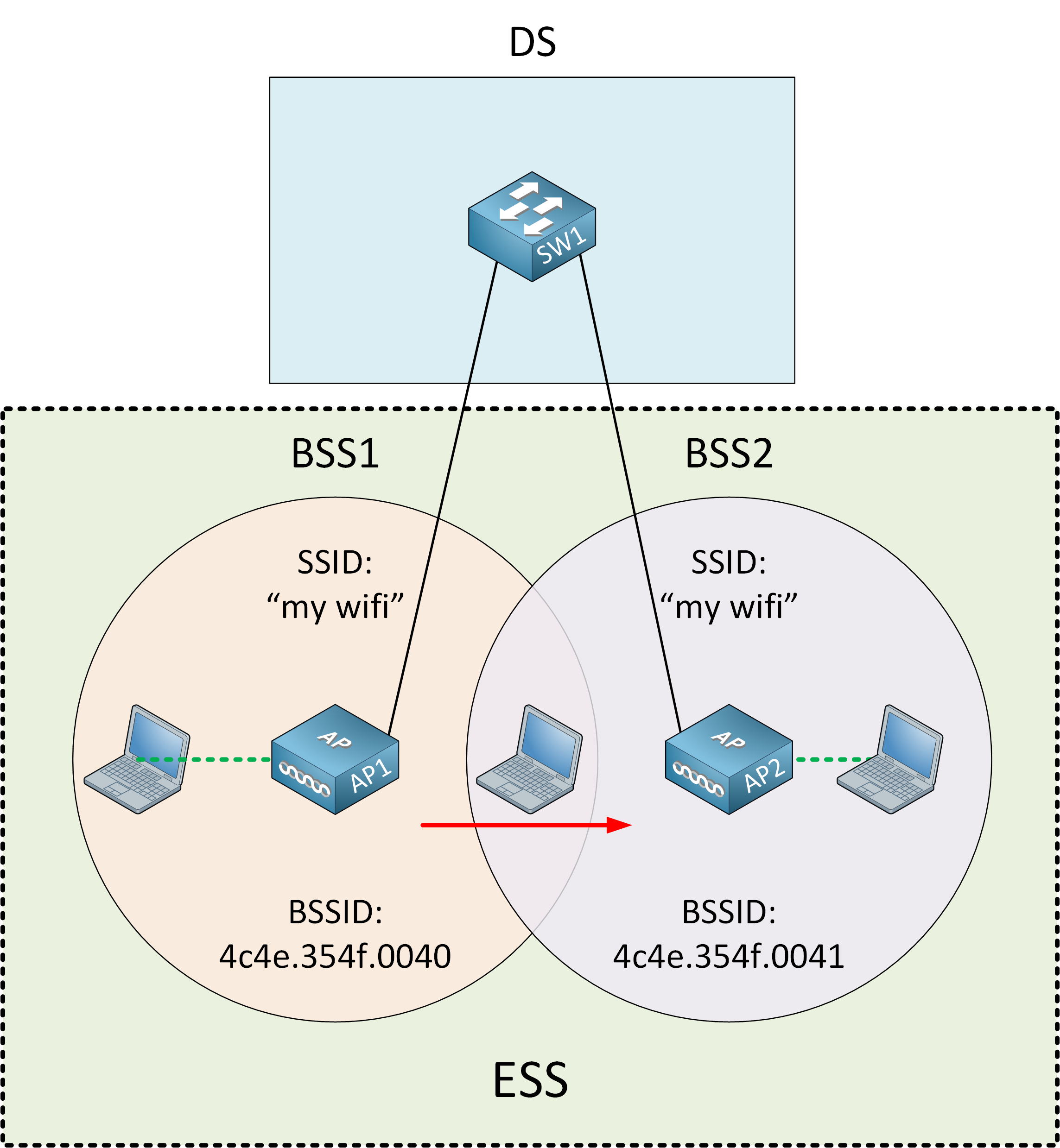
APs work together. For case, if y'all acquaintance with one AP and you lot walk effectually the building, you won't disconnect. The wireless client will automatically "jump" from one AP to another AP. We call this roaming. To make this a seamless experience, nosotros demand an overlap between APs.
Each AP offers its own BSS and uses a dissimilar channel to prevent interference between APs.
Mesh Bones Service Set (MBSS)
If you desire to provide a wireless network for a large surface area, similar a urban center, then it'south non piece of cake to connect each AP to a wired network.
Instead, you could build a mesh network, also known equally a Mesh Basic Service Set (MBSS). With a mesh network, we bridge wireless traffic from one AP to some other. Mesh APs unremarkably take multiple radios. One radio is for backhaul traffic of the mesh network betwixt APs; the other radio is to maintain a BSS for wireless clients on another channel.
At least i AP is connected to the wired network; we telephone call this the Root AP (RAP). The other APs are Mesh APs (MAP) and are simply connected through the wireless backhaul.
How Many Access Points Are Used By A Basic Service Set (Bss)?,
Source: https://networklessons.com/cisco/ccna-200-301/wireless-lan-802-11-service-sets
Posted by: rachalbeenarile.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Many Access Points Are Used By A Basic Service Set (Bss)?"
Post a Comment